European Economic and Diplomatic Status
Throughout the entirety of The American Civil War, both the Union and Confederacy sought various goals with European Powers. The Union wanted no European Power to enter the war while the Confederacy wanted European Powers to recognize itself and join on their behalf. Because of this diplomatic battle and the Anaconda Plan, a variety of European Countries were affected. However, the effect of The American Civil War on these countries were not significant enough to change economic decisions, but rather slightly strengthened diplomatic ties decades after the American Civil War.
United Kingdom
Economic Effects
The United Kingdom was slightly affected in the early stages of the American Civil War and Union Blockade. The United States accounted for 80% of cotton imports to Britain, and many businesses were dependent on such imports. The Union Blockade prevented such imports of cotton to Britain, and at first heavily wore down business in the clothing or cotton industry. This sparked diplomatic tension between the United Kingdom and the United States. However, this tension and effect on the British Economy did not last, as Britain had a surplus of cotton, and imports from the British East Indies, Egypt, and Brazil soon filled the role the United States provided previously. Furthermore, runners of the blockade managed to smuggle cotton down to Central America, in which it would be exported to Britain. Overall, the American Civil War did not prove to have any significant effect on British Economy. The Union Blockade prevented Confederate States from exporting cotton, allowing other countries to profit from the cotton industry.
Diplomatic Effects
While the United Kingdom’s economy did not suffer, certain diplomatic tensions arose during The American Civil War. After the emplacement of the Union Blockade, any ships that imposed to run the blockade would be chased down and caught by Union ships. One such event was The Trent, in which two British ambassadors who had slipped past the blockade were trying to leave. They were caught and held prisoner by the Union. This sparked diplomatic tension between the United Kingdom and the Union, and raised the possibility that Britain could possibly join the war. However, this diplomatic crisis was quickly resolved in the release of the two British ambassadors. Overall, The American Civil War affected diplomatic decisions of Britain and the United States for years to come. The United States's actions of defying neutrality affects future decisions while the United Kingdom’s actions of standing firm in agreements affected future conquests.

France
Economic Effects
France suffered little economically from The American Civil War. Even before the war, France’s naval fleet was lacking, and it’s economy was not dependent on the cotton industry. However, the country had a dependency of imported cotton goods, in which the mass majority of were from the British Commonwealth. Although the Union Blockade did affect Britain, in turn affecting France’s imports of cotton goods, it did not last or affect anyone in a significant way. This is because of the smuggled cotton from the south and other cotton goods coming from Egypt, Brazil, and the British East Indies. Overall, France was not affected in any large or long lasting way, and what little effects recovered quickly.
Diplomatic Effects
While France sent a formal letter not recognizing the Confederacy, there were little other diplomatic effects. France did not meet with any Confederate diplomats, and did not join or partake in the war directly. No event angered or convinced the French to join the Union or Confederacy, as France expressed its neutrality during the internal conflict. Furthermore, france was going through more pressing matters and events, such as the french intervention of Mexico, and the upcoming Franco-Prussian war.
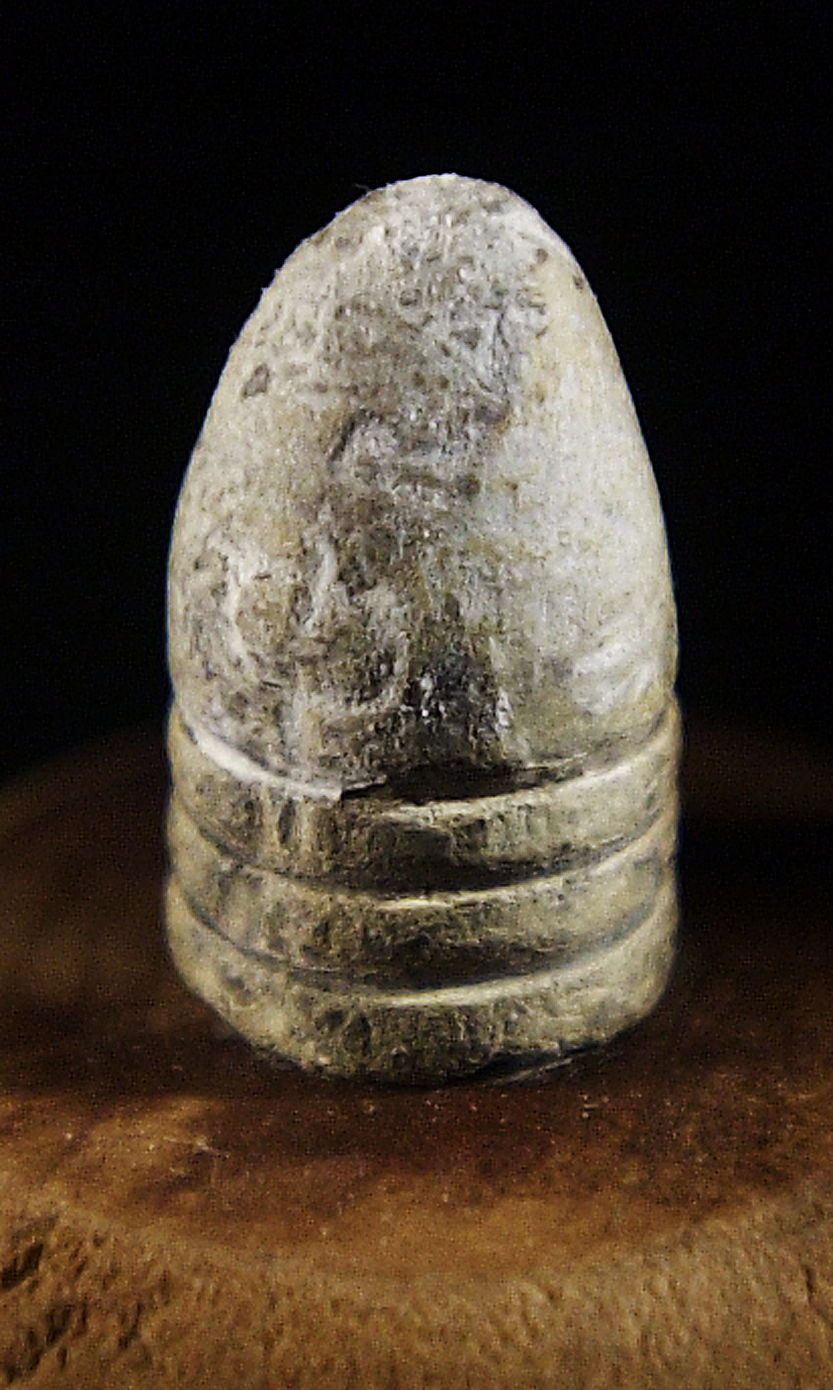
Indirect Involvement
France did however contribute to the Civil War with the deadliest technology used by both sides of the war; The Minie Ball. While neither side bought directly from France, nor did it affect any diplomatic standpoints, the Minie Ball contributed to 90% of all casualties during the Civil War. Created by the French Officer Claude-Etienne Minié, it was deadly and accurate at far ranges, reducing the effectiveness of cavalry.
Italian States
Diplomatic Effects
The Italian States suffered minimal economic effects of The American Civil War. At the time, the Italian States were no cotton monopoly, and cotton had very little contribution to the overall economy of the states. The mass majority of the cotton imported into the Italian States came from Egypt, Britain, and other various countries. Although the Union Blockade had restricted some cotton flow to Britain, it was such a minimal amount to actually influence economic decisions within the Italian States.
Indirect Involvement
The Italian States suffered very few diplomatic consequences or effects from The American Civil War. At the time, the Italian States were struggling in other diplomatic tensions, such as the Italian Unification, assassination of Napoleon III, and various other events. While In the late 19th century many Italians emigrated to the United States, it was not because of any economic or diplomatic event that triggered this mass emigration.